Evaluation of side effects of radiofrequency capacitive hyperthermia with magnetite on the blood vessel walls of tumor metastatic lesion surrounding the abdominal large vessels: an agar phantom study
Main Article Content
Abstract
Background
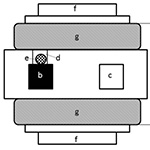
Magnetite used in an 8-MHz radiofrequency (RF) capacitive heating device can increase the temperature of a specific site up to 45°C. When treating a metastatic lesion around large abdominal vessels via hyperthermia with magnetite, heating-induced adverse effects on these vessels need to be considered. Therefore, this study examined hyperthermia-induced damage to blood vessel walls in vitro.Methods
A large agar phantom with a circulatory system consisting of a swine artery and vein connected to a peristaltic pump was prepared. The blood vessels were placed on the magnetite-containing agar piece. Heating was continued for 30 min at 45°C. After heating, a histological study for injury to the blood vessels was performed.Results
The inner membrane temperature did not reach 45°C due to the cooling effect of the blood flow. In the heated vessels, vascular wall collagen degenerated and smooth muscle cells were narrowed; however, no serious changes were noted in the vascular endothelial cells or vascular wall elastic fibers. The heated vessel wall was not severely damaged; this was attributed to cooling by the blood flow.Conclusions
Our findings indicate that RF capacitive heating therapy with magnetite may be used for metastatic lesions without injuring the surrounding large abdominal vessels.Article Details
How to Cite
KAWAI, Noriyasu et al.
Evaluation of side effects of radiofrequency capacitive hyperthermia with magnetite on the blood vessel walls of tumor metastatic lesion surrounding the abdominal large vessels: an agar phantom study.
Vascular Cell, [S.l.], v. 6, n. 1, p. 15, july 2014.
ISSN 2045-824X.
Available at: <https://vascularcell.com/index.php/vc/article/view/10.1186-2045-824X-6-15>. Date accessed: 13 mar. 2026.
doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/2045-824X-6-15.
Section
Original Research