Arteriogenic therapy based on simultaneous delivery of VEGF-A and FGF4 genes improves the recovery from acute limb ischemia
Main Article Content
Abstract
Background
Gene therapy stimulating the growth of blood vessels is considered for the treatment of peripheral and myocardial ischemia. Here we aimed to achieve angiogenic synergism between vascular endothelial growth factor-A (VEGF-A, VEGF) and fibroblast growth factor 4 (FGF4) in murine normoperfused and ischemic limb muscles.Methods
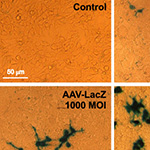
Adeno-associated viral vectors (AAVs) carrying β-galactosidase gene (AAV-LacZ), VEGF-A (AAV-VEGF-A) or two angiogenic genes (AAV-FGF4-IRES-VEGF-A) were injected into the normo-perfused adductor muscles of C57Bl/6 mice. Moreover, in a different experiment, mice were subjected to unilateral hindlimb ischemia by femoral artery ligation followed by intramuscular injections of AAV-LacZ, AAV-VEGF-A or AAV-FGF4-IRES-VEGF-A below the site of ligation. Post-ischemic blood flow recovery was assessed sequentially by color laser Doppler. Mice were monitored for 28 days.Results
VEGF-A delivered alone (AAV-VEGF-A) or in combination with FGF4 (AAV-FGF4-IRES-VEGF-A) increased the number of capillaries in normo-perfused hindlimbs when compared to AAV-LacZ. Simultaneous overexpression of both agents (VEGF-A and FGF4) stimulated the capillary wall remodeling in the non-ischemic model. Moreover, AAV-FGF4-IRES-VEGF-A faster restored the post-ischemic foot blood flow and decreased the incidence of toe necrosis in comparison to AAV-LacZ.Conclusions
Synergy between VEGF-A and FGF4 to produce stable and functional blood vessels may be considered a promising option in cardiovascular gene therapy.Article Details
How to Cite
JAZWA, Agnieszka et al.
Arteriogenic therapy based on simultaneous delivery of VEGF-A and FGF4 genes improves the recovery from acute limb ischemia.
Vascular Cell, [S.l.], v. 5, n. 1, p. 13, july 2013.
ISSN 2045-824X.
Available at: <https://vascularcell.com/index.php/vc/article/view/10.1186-2045-824X-5-13>. Date accessed: 21 feb. 2026.
doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/2045-824X-5-13.
Section
Original Research